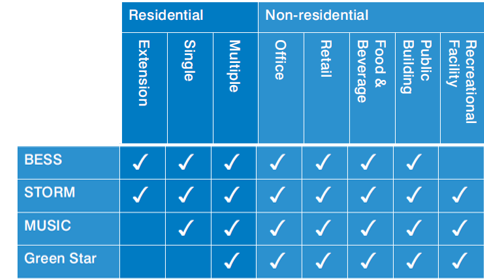
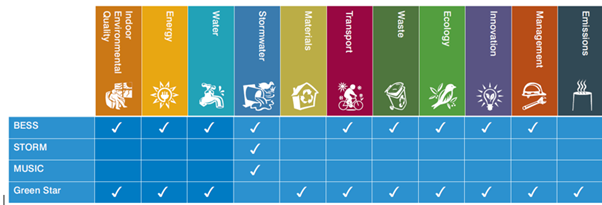
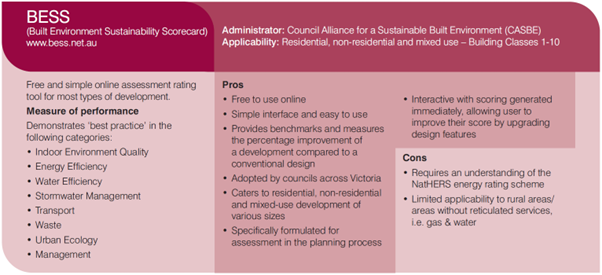
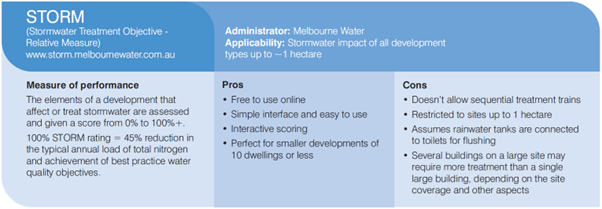
An SDA is a sustainability assessment of a proposed development undertaken at the planning stage.
Generally, an SDA can be prepared by the permit applicant (using the above online tools). The more complex the proposal however, the more involved the assessment must be.
Qualified professionals (such as an ESD Consultant) should be engaged to assist with more complex assessments.
The SDA supports the planning application by demonstrating how the proposal responds to 10 key sustainable building categories, as listed below.
By clicking on a category title you will be redirected to CASBE’s related fact sheet.
1.0 - Indoor Environmental Quality
Objective: To achieve healthy indoor environmental quality for the well-being of building occupants.
Examples of design initiatives:
- Maximise daylight access;
- Thermal comfort; and
- Natural ventilation.
1.2 - Daylight
Objective: To increase occupant comfort and well-being with reduced energy demand.
Examples of design initiatives:
- Maximise Orientation;
- Optimise window size and location; and
- Glazing selection.
1.2 - Natural Ventilation
Objective: Providing fresh air and passive cooling to increase occupant comfort, health and wellbeing while reducing energy demand.
Examples of design initiatives:
- Number & location of windows;
- Size and depth of internal space; and
- Favour natural crossflow and passive ventilation.
2.0 - Energy Efficiency
Objectives: To ensure efficient use of energy; To reduce total operating greenhouse gas emissions; and To reduce peak energy demand.
Examples of design initiatives:
- Building fabric above the minimum Building Code of Australia (BCA) requirements;
- Renewable energy generation (and storage); and
- Efficient heating and cooling services.
2.1 - External Shading
Examples of design initiatives:
- Effective shading devices;
- Adjustable devices for east and west aspects;
- Fixed devices to 45% rule for north aspects.
2.2 - Building Envelope Performance
Objectives: Increasing occupancy comfort, health and well-being while reducing energy demand and increasing your building’s value and construction standard.
Examples of design initiatives:
- Thermally efficient walls, windows, doors, floor and roof;
- Best performing Glazing & Framing;
- Airtight and thermally bridged; and
- Acoustic / noise reducing.
2.3 - Zero Carbon Development
Objectives: To ensure that new buildings and significant alterations and additions are planned and designed in a manner which incorporate Environmentally Sustainable Development (ESD) principles, mitigates and adapts to climate change, protects the natural environment, reduces resource consumption and supports the health and wellbeing of future occupants.
Examples of design initiatives:
- Renewable Energy;
- All-electric (No gas) & energy efficient appliances; and
- Low-zero carbon materials & waste minimisation.
3.0 - Water Efficiency
Objectives: To ensure the efficient use of water; To reduce total operating potable water use; and To encourage the appropriate use of alternative water sources.
Examples of design initiatives:
- Use of efficient fixtures and fittings;
- Avoid use of mains water for irrigation; and
- Re-use water/implement greywater systems
4.0 - Stormwater Management
Objectives: To reduce the impact of stormwater run-off; To improve the water quality of stormwater run-off; To achieve best practice stormwater quality outcomes; and To incorporate the use of water sensitive urban design, including rainwater re-use.
Examples of initiatives:
- Minimise watercourse pollution;
- Maximise stormwater capture (including by using rainwater tanks); and
- Maximise on-site rainwater re-use, including in the service of toilets and to irrigate landscaped areas
4.1 - Site Permeability
Objectives: To minimise stormwater run-off by permitting rainwater to be absorbed into the soil. A lack of permeability increases flooding in urban areas during storm events affecting infrastructure and buildings.
Examples of initiatives:
- Maximise natural ground surfaces;
- Permeable surfaces below and/or around paving or decking;
- Permeable paving.
5.0 - Building Materials
Objective: To minimise environmental impacts by encouraging the use of materials with a favourable lifecycle assessment
Examples of initiatives:
- Use materials with low embodied energy;
- Use materials with recycled content; and
- Consider the future recyclability of materials
6.0 - Transport
Objectives: To minimise car dependency and to ensure that the built environment is designed to promote the use of public transport, walking and cycling.
Examples of initiatives:
- The provision of convenient and secure bicycle storage;
- The provisions of shower and associated facilities within work places; and
- Green Travel Plans for building users and their visitors
6.1 - Electric Vehicles
Objectives: Electric vehicle integration in new developments. Reduction in emissions and costs.
Examples of initiatives:
- Provision of charging infrastructure;
- In apartments and commercial developments; and
- Increase the number of public/community charging stations;
- Transition to renewable energy powered EV’s.
7.0 - Waste Management
Objective: To ensure waste avoidance reuse and recycling during the construction and operational stages of development.
Examples of initiatives:
- Adoption of demolition and construction material recycling target;
- Provision of construction Waste Management Plan (WMP); and
- Provision of operational WMP
8.0 - Urban Ecology
Objectives: To protect and enhance biodiversity; To provide natural habitats and minimise the urban heat island effect. To encourage the retention of significant trees and the planting of indigenous vegetation.
Examples of initiatives:
- Maintaining and/or enhancing the biodiversity values of a site;
- Encouraging new biodiversity areas; and
- Incorporating resident amenity spaces
8.1 - Green Roofs, Walls and Facades
Objectives: To cool a building and surrounds; to help reduce stormwater runoff; and to improve well-being and increase biodiversity.
Examples of initiatives:
- Green roofs are raised vegetation beds;
- Green facades to grow plants up and across a building; and
- Green walls are vertical gardens.
9.0 - Innovation
Objective: To encourage innovative technology, design and processes in all development so as to positively influence the sustainability of buildings.
Examples of initiatives:
- Significant enhancements to best practice sustainable design standards;
- Introduction of new technologies; and
- Passive design
10.0 - Construction and Building Management
Objective: To encourage a holistic and integrated design and construction process and ongoing high performance of buildings
Examples of initiatives:
- Circulation of Building User Guide explaining to occupants the ESD initiatives of the building;
- Preparation of operational Environmental Management Plans (EMPs); and
- Ensuring all contractors have valid environmental management accreditation